Non-linear elasticity
Algorithm to solve the non-linear elasticity problem using a minimization technique.
Problem
Let $\Omega \subset \mathbb{R}^{3}$ denotes a hyperelastic material and $\partial \Omega= \Gamma_{0} \cup \Gamma_{1}$ its boundary, $\Gamma_{0}$ and $\Gamma_{1}$ denote respectively the disjoint parts of the boundary ($\Gamma_{0} \cap \Gamma_{1}= \emptyset$) where a null displacement and a surface traction $\mathbf{t}$ are applied.
The problem is to find the displacement field $\mathbf{u}$ of the body $\Omega$, which minimizes the total potential energy $\mathcal{E}$ given by:
$ \displaystyle{ \mathcal{E}(\mathbf{v})= \int_{\Omega} \Psi \, dV - \int_{\Gamma_{1}} \mathbf{t}.\mathbf{v} \, dA } $
Therefore:
$ \displaystyle{ \mathbf{u}= \underset{\mathbf{v} \in \mathcal{A}}{\text{argmin}}(\mathcal{E}(\mathbf{v})) } $
Where $\Psi$ is the strain energy function and $\mathcal{A}$ is the admissible displacements set defined by:
$ \displaystyle{ \mathcal{A}=\left\lbrace \mathbf{v} \in \left( H^{1}(\Omega)\right)^{3} \; ; \; \mathbf{v}=0 \; \text{on} \; \Gamma_{0} \right\rbrace } $
Algorithms
Material parameters
File NeoHookean.idp
real c10 = 1.2345;
real c01 = 0.;
real nu = 0.499;
real K = 6.*(c01+c10)/(3.*(1.-2.*nu));
// The energy density function is equal to : W(I1,I2,I3) = c1.I1.I3^(-1/3) + c2.I3 + c3.I3^(1/2) + c4
real c1 = c10;
real c2 = K/2.;
real c3 = -K;
real c4 = -3.*c10 + K/2.;
// The energy density
macro W(I)
(
c1*I[0]*(I[2]^(-1./3.)) + c2*I[2] + c3*(I[2]^(1./2.)) + c4
) //
// The first differential of the energy density
macro dW(I, dI)
(
c1*(I[2]^(-1./3.))*dI[0] + c1*I[0]*(-1./3.)*(I[2]^(-4./3.))*dI[2] + c2*dI[2]
+ c3*(1./2.)*(I[2]^(-1./2.))*dI[2]
) //
// The second differential of the energy density
macro ddW(I, dI, dII)
(
c1*(-1./3.)*(I[2]^(-4./3.))*dI[0]*dII[2]
+ c1*(-1./3.)*(I[2]^(-4./3.))*dI[2]*dII[0]
+ c1*I[0]*(-1./3.)*(-4./3.)*(I[2]^(-7./3.))*dI[2]*dII[2]
+ c3*(1./2.)*(-1./2.)*(I[2]^(-3./2.))*dI[2]*dII[2]
) //Elasticity law
Definition of the elasticity law in 2D.
File ElasticLaw2d.idp
macro C2(d)
[
1. + 2.*dx(d[0]) + dx(d[0])*dx(d[0]) + dx(d[1])*dx(d[1]),
1. + 2.*dy(d[1]) + dy(d[0])*dy(d[0]) + dy(d[1])*dy(d[1]),
dy(d[0]) + dx(d[1]) + dx(d[0])*dy(d[0]) + dx(d[1])*dy(d[1])
] //
macro dC2(d, dd)
[
2.*dx((dd)[0]) + 2.*dx((dd)[0])*dx(d[0]) + 2.*dx((dd)[1])*dx(d[1]),
2.*dy((dd)[1]) + 2.*dy((dd)[0])*dy(d[0]) + 2.*dy((dd)[1])*dy(d[1]),
dy((dd)[0]) + dx((dd)[1]) + dx((dd)[0])*dy(d[0]) + dx((dd)[1])*dy(d[1])
+ dx(d[0])*dy((dd)[0]) + dx(d[1])*dy((dd)[1])
] //
macro ddC2(dd, ddd)
[
2.*dx((dd)[0])*dx((ddd)[0]) + 2.*dx((dd)[1])*dx((ddd)[1]),
2.*dy((dd)[0])*dy((ddd)[0]) + 2.*dy((dd)[1])*dy((ddd)[1]),
dx((dd)[0])*dy((ddd)[0]) + dx((dd)[1])*dy((ddd)[1])
+ dx((ddd)[0])*dy((dd)[0]) + dx((ddd)[1])*dy((dd)[1])
] //
macro I2C(C)
[
C[0] + C[1] + 1.,
C[0]*C[1] + C[1] + C[0] - C[2]*C[2],
C[0]*C[1] - C[2]*C[2]
] //EOM
macro dI2C(C, dC)
[
dC[0] + dC[1] ,
dC[0]*C[1] + dC[1] + dC[0] - 2.*dC[2]*C[2] + C[0]*dC[1],
dC[0]*C[1] + C[0]*dC[1] - 2.*C[2]*dC[2]
] //
macro ddI2C(dC, ddC)
[
0.*dC[0]*ddC[0],
dC[0]*ddC[1] - 2.*dC[2]*ddC[2] + ddC[0]*dC[1],
dC[0]*ddC[1] + ddC[0]*dC[1] - 2.*ddC[2]*dC[2]
] //
macro I2d(d) I2C(C2(d)) //
macro dI2d(d, dd) dI2C(C2(d), dC2(d, dd)) //
macro ddI2d(d, dd, ddd) (ddI2C(dC2(d, dd), dC2(d, ddd)) + dI2C(C2(d), ddC2((dd), (ddd)))) //
macro W2d(d) W(I2d(d)) //
macro dW2d(d, dd) dW(I2d(d), dI2d(d, dd)) //
macro ddW2d(d, dd, ddd) (ddW(I2d(d), dI2d(d, dd), dI2d(d, ddd)) + dW(I2d(d), ddI2d(d, dd, ddd))) //Minimization algorithm
load "ff-Ipopt"
include "ElasticLaw2d.idp"
include "NeoHookean.idp"
// Dimension constants
real L = 0.5;
real l = 1.;
real cx = 0;
real cy = -l/2;
// Discretization constants
int Nx = 5;
int Ny = 2*Nx;
real f1 = 0, f2 = -0.876;
int[int] labs = [1, 2, 3, 4];
mesh Th = square(Nx, Ny, [L*x+cx, l*y+cy], label=labs, flags=1);
fespace Wh(Th, [P1, P1]);
//The total potential energy
func real iW (real[int] &D) {
Wh [DDx, DDy];
DDx[] = D;
real res = int2d(Th)(W2d([DDx, DDy])) - int1d(Th,3)([DDx, DDy]'*[f1, f2]);
return res;
}
//The gradient of the energy
func real[int] idW (real[int] &D) {
Wh [DDx, DDy];
DDx[] = D;
varf dWW ([Dx, Dy], [Vx, Vy])
= int2d(Th)(
dW2d([DDx, DDy], [Vx, Vy])) - int1d(Th, 3)([Vx, Vy]'*[f1, f2]);
real[int] idWW = dWW(0, Wh);
return idWW;
}
//The Hessian of the energy
matrix iddWW;
func matrix iddW (real[int] &D) {
Wh [DDx, DDy];
DDx[] = D;
varf ddWW ([Dx, Dy], [Vx, Vy])
= int2d(Th)(
ddW2d([DDx, DDy], [Dx, Dy], [Vx, Vy])
);
iddWW = ddWW(Wh, Wh);
return iddWW;
}
// Boundary conditions
Wh [ub1, ub2] = [1e19, 1e19]; // Unbounded in interior
Wh [lb1, lb2] = [-1e19, -1e19]; // Unbounded in interior
varf vGamma1([Dx, Dy], [v1, v2]) = on(1, Dx=1, Dy=1); // Boundary conditions
varf vGamma4([Dx, Dy], [v1, v2]) = on(4, Dx=1, Dy=1); // Boundary conditions
real[int] onGamma1 = vGamma1(0, Wh);
real[int] onGamma4 = vGamma4(0, Wh);
Wh [ubb1, ubb2] = [1e19, 0.];
Wh [lbb1, lbb2] = [-1e19, 0.];
Wh [ubb4, ubb5] = [0., 1e19];
Wh [lbb4, lbb5] = [0., -1e19];
ub1[] = onGamma1 ? ubb1[] : ub1[]; // enforcing the boundary condition
lb1[] = onGamma1 ? lbb1[] : lb1[];
ub1[] = onGamma4 ? ubb4[] : ub1[]; // enforcing the boundary condition
lb1[] = onGamma4 ? lbb4[] : lb1[];
for (int i = 0; i < ub1[].n; i++)
if (onGamma1[i] && onGamma4[i]){ ub1[][i] = 0.; lb1[][i] = 0.; }
Wh [Dx, Dy] = [0., 0.];
IPOPT(iW, idW, iddW, Dx[], lb=lb1[], ub=ub1[]); // Minimize
mesh Thm = movemesh(Th, [x+Dx, y+Dy]);
[Dx, Dy] = [Dx, Dy];
plot([Dx, Dy]);| Result - Deformation and displacement field |
|---|
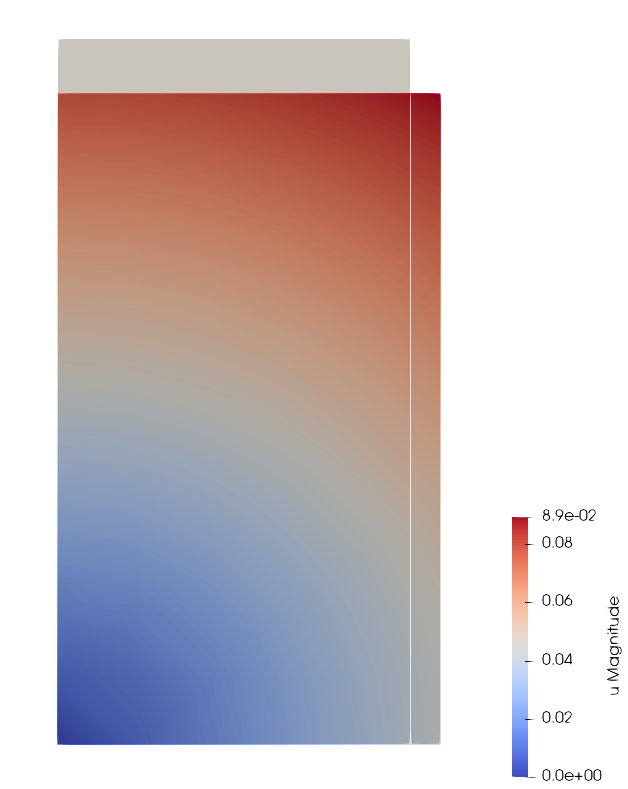 |
Validation
See FRICTIONLESS CONTACT PROBLEM FOR HYPERELASTIC MATERIALS WITH INTERIOR POINT OPTIMIZER, H. Houssein, S. Garnotel, F. Hecht (upcoming article)
Authors
Author: Houssam Houssein
